

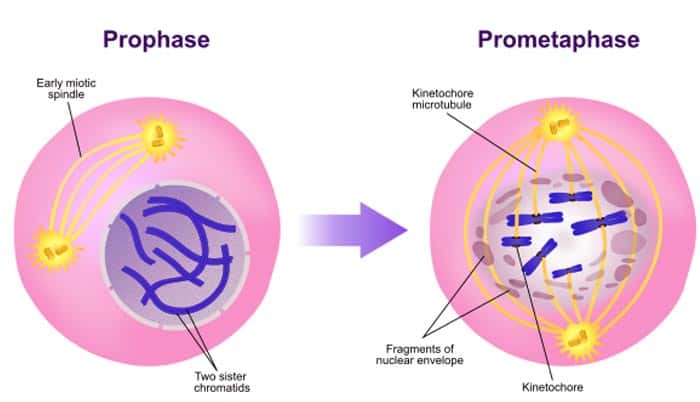

The chromosomes condense into compact structures. The centrosomes organise the production of microtubules that form the spindle fibres that constitute the mitotic spindle. A structure known as the centrosome duplicates itself to form two daughter centrosomes that migrate to opposite ends of the cell. The nuclear membrane breaks down to form a number of small vesicles and the nucleolus disintegrates. Mitosis, although a continuous process, is conventionally divided into five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. In the adult organism, mitosis plays a role in cell replacement, wound healing and tumour formation. Mitotic divisions of the zygote and daughter cells are then responsible for the subsequent growth and development of the organism. In diploid multicellular organisms sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two haploid gametes to produce a diploid zygote. In some single-celled organisms mitosis forms the basis of asexual reproduction. This separation of the genetic material in a mitotic nuclear division (or karyokinesis) is followed by a separation of the cell cytoplasm in a cellular division (or cytokinesis) to produce two daughter cells. The replicated chromosomes are attached to a 'mitotic apparatus' that aligns them and then separates the sister chromatids to produce an even partitioning of the genetic material. In actively dividing animal cells, the whole process takes about one hour. Chromosomes replicated during the S phase are divided in such a way as to ensure that each daughter cell receives a copy of every chromosome. Mitosis is a form of eukaryotic cell division that produces two daughter cells with the same genetic component as the parent cell. The period between mitotic divisions - that is, G1, S and G2 - is known as interphase.A nuclear division (mitosis) followed by a cell division (cytokinesis). Metabolic changes assemble the cytoplasmic materials necessary for mitosis and cytokinesis. Each chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids. DNA synthesis replicates the genetic material. At a certain point - the restriction point - the cell is committed to division and moves into the S phase. Metabolic changes prepare the cell for division.
Prophase 1 mitosis series#
Actively dividing eukaryote cells pass through a series of stages known collectively as the cell cycle: two gap phases (G1 and G2) an S (for synthesis) phase, in which the genetic material is duplicated and an M phase, in which mitosis partitions the genetic material and the cell divides.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
